Page 10 - Annual Review 2021 full
P. 10
Indian National Shipowners’ Association
In COP26 held recently in Glasgow has Invited sea, inland waterways or coastal vessels. Such
Parties to consider further actions to reduce by 2030 vessels have little storage capacity on board but
non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gas emissions, can refuel frequently or they can run on batteries.
including methane.
It is an entirely different ballgame when it comes to
Mid and long-term fuel mix pathway deep-sea shipping. Such vessels need a fuel that
Fuels like LPG, methanol as well as bio-derived or does not take away too much cargo carrying space.
synthetic LPG/methanol have similar properties The International Energy Agency has also stated in
to diesel oil and thus are much less demanding a new report that biofuels, ammonia and hydrogen
in terms of new infrastructure and technologies will meet more than 80% of shipping fuel needs by
onboard and can be utilised with minimal changes 2070, using around 13% of the world’s hydrogen
to current ship designs.
production, with ammonia the outright leader.
“More than 60% of the emissions reductions in 2070
There is currently no proven deep-sea, long haul, come from technologies that are not commercially
zero emissions solution. While there are several available today, the Paris-based agency has
options available they are best matched to short-
predicted.
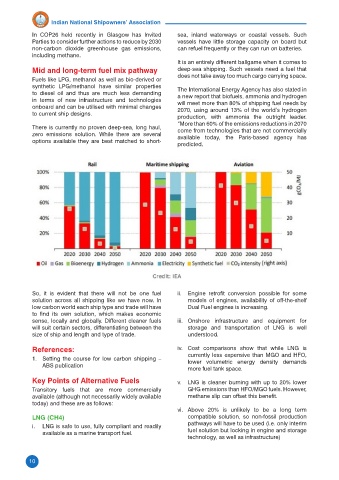
So, it is evident that there will not be one fuel ii. Engine retrofit conversion possible for some
solution across all shipping like we have now. In models of engines, availability of off-the-shelf
low carbon world each ship type and trade will have Dual Fuel engines is increasing.
to find its own solution, which makes economic
sense, locally and globally. Different cleaner fuels iii. Onshore infrastructure and equipment for
will suit certain sectors, differentiating between the storage and transportation of LNG is well
size of ship and length and type of trade. understood.
References: iv. Cost comparisons show that while LNG is
1. Setting the course for low carbon shipping – currently less expensive than MGO and HFO,
lower volumetric energy density demands
ABS publication
more fuel tank space.
Key Points of Alternative Fuels v. LNG is cleaner burning with up to 20% lower
Transitory fuels that are more commercially GHG emissions than HFO/MGO fuels. However,
available (although not necessarily widely available methane slip can offset this benefit.
today) and these are as follows:
vi. Above 20% is unlikely to be a long term
LNG (CH4) compatible solution, so non-fossil production
i. LNG is safe to use, fully compliant and readily pathways will have to be used (i.e. only interim
available as a marine transport fuel. fuel solution but locking in engine and storage
technology, as well as infrastructure)
10